Which Institution Offers Banking Services But Do Not Accept Deposits Like Traditional Banks
Understanding Money and Financial Institutions
132 U.Southward. Financial Institutions
- What are the cardinal financial institutions, and what role do they play in the process of financial intermediation?
The well-developed fiscal system in the United states of america supports our high standard of living. The organization allows those who wish to infringe money to exercise then with relative ease. It likewise gives savers a diversity of ways to earn interest on their savings. For instance, a computer company that wants to build a new headquarters in Atlanta might exist financed partly with the savings of families in California. The Californians deposit their money in a local financial institution. That institution looks for a profitable and safe style to use the coin and decides to brand a existent estate loan to the computer visitor. The transfer of funds from savers to investors enables businesses to expand and the economy to grow.
Households are important participants in the U.S. financial system. Although many households borrow money to finance purchases, they supply funds to the fiscal system through their purchases and savings. Overall, businesses and governments are users of funds. They borrow more money than they save.
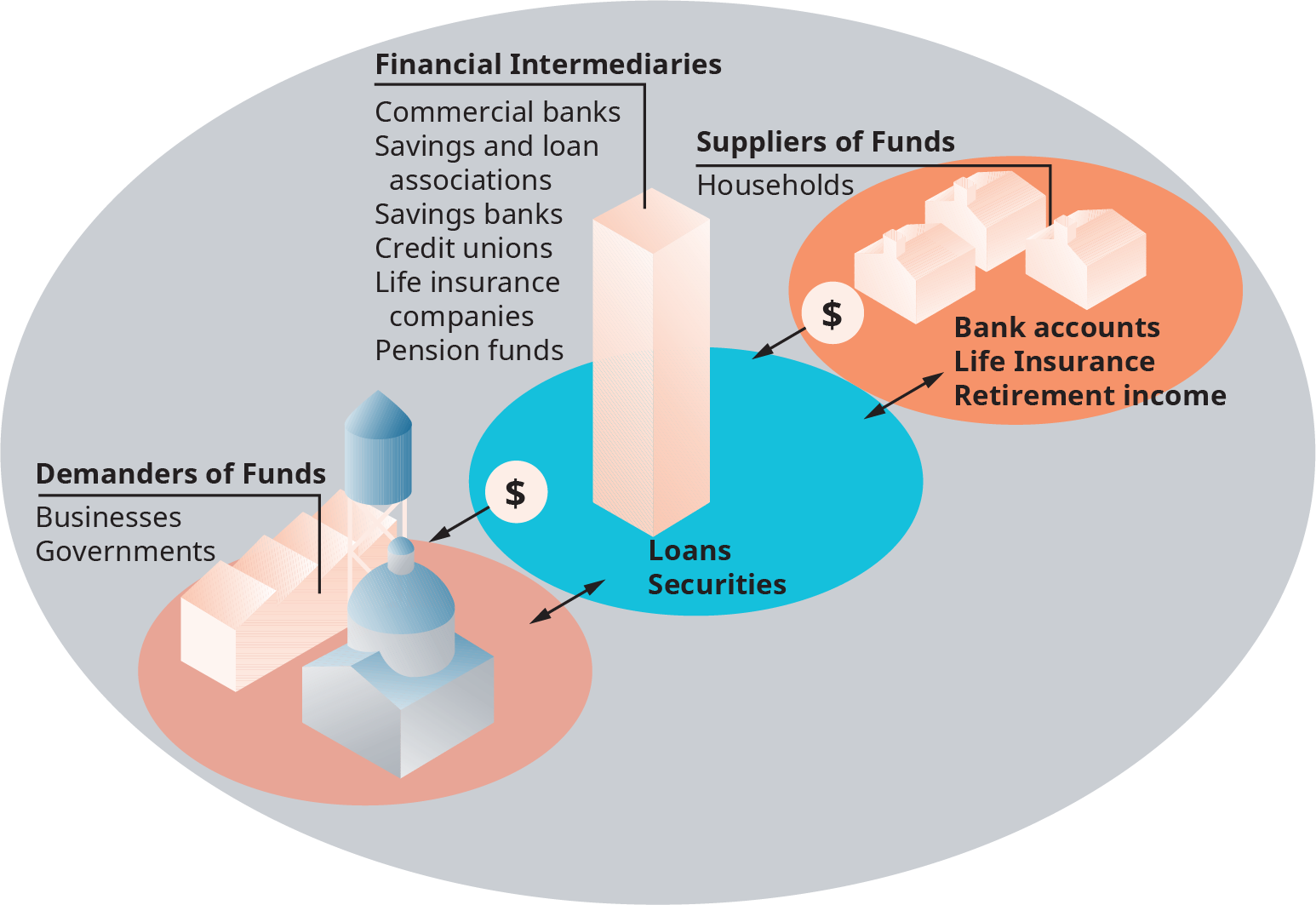
Sometimes those who accept funds deal directly with those who want them. A wealthy realtor, for case, may lend money to a customer to buy a house. Most often, financial institutions act as intermediaries—or go-betweens—betwixt the suppliers and demanders of funds. The institutions accept savers' deposits and invest them in financial products (such as loans) that are expected to produce a render. This process, called financial intermediation, is shown in (Figure). Households are shown every bit suppliers of funds, and businesses and governments are shown every bit demanders. However, a single household, business, or authorities can exist either a supplier or a demander, depending on the circumstances.
Financial institutions are the heart of the financial organisation. They are user-friendly vehicles for fiscal intermediation. They can be divided into ii broad groups: depository institutions (those that accept deposits) and nondepository institutions (those that practice not take deposits).
The Financial Intermediation Process*
Only the dominant suppliers and demanders are shown here. Conspicuously, a single household, business, or government can exist either a supplier or demander, depending on circumstances. (Attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, under CC BY four.0 license.)
Depository Financial Institutions
Not all depository fiscal institutions are alike. Most people call the place where they save their money a "bank." Some of those places are indeed banks, just other depository institutions include thrift institutions and credit unions.
Commercial Banks
A commercial bank is a profit-oriented financial institution that accepts deposits, makes concern and consumer loans, invests in government and corporate securities, and provides other financial services. Commercial banks vary greatly in size, from the "money center" banks located in the nation's financial centers to smaller regional and local customs banks. As a upshot of consolidations, small banks are decreasing in number. A big share of the nation's cyberbanking business is at present held by a relatively pocket-size number of large banks. There are approximately v,011 commercial banks in the United states, accounting for nearly $16 trillion in assets and $9 trillion in full liabilities.
"Statistics at a Glance as of June xxx, 2017," https://world wide web.fdic.gov, accessed September seven, 2017.
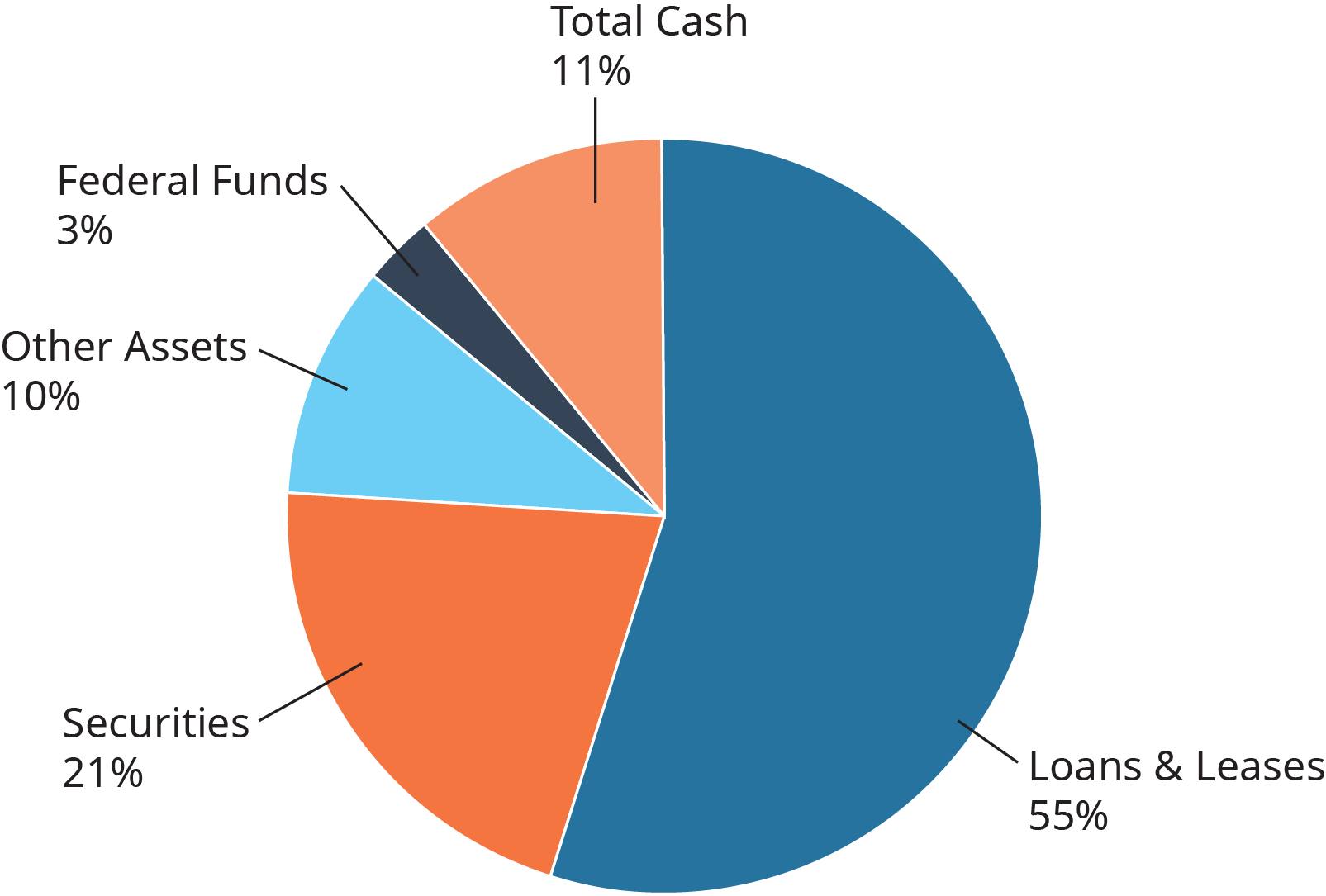
Banks concord a variety of assets, equally shown in the diagram in (Figure).
(Figure) lists the elevation 10 insured U.S.-chartered commercial banks, based on their consolidated assets.
Assets of FDIC-Insured Commercial Banks, 2017
Source: "FDIC: Statistics on Depository Institutions Written report for Commercial Banks as of half-dozen/xxx/17," https://www5.fdic.gov, accessed September 7, 2017.
Customers' deposits are a commercial bank's major source of funds, the chief use for which is loans. The difference betwixt the involvement the depository financial institution earns on loans and the involvement it pays on deposits, plus fees information technology earns from other financial services, pays the bank's costs and provides a turn a profit.
Commercial banks are corporations owned and operated by individuals or other corporations. They tin can be either national or state banks, and to practice business organization, they must get a bank charter—an operating license—from a land or federal authorities. National banks are chartered past the Comptroller of the Currency, who is part of the U.S. Treasury Department. These banks must belong to the Federal Reserve Organisation and must conduct insurance on their deposits from the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. State banks are chartered by the state in which they are based. Mostly, land banks are smaller than national banks, are less closely regulated than national banks, and are non required to vest to the Federal Reserve System.
Thrift Institutions
A thrift institution is a depository institution formed specifically to encourage household saving and to make domicile mortgage loans. Thrift institutions include savings and loan associations (Due south&Ls) and savings banks. Due south&Ls keep large percentages of their assets in dwelling mortgages. Compared with S&Ls, savings banks focus less on mortgage loans and more on stock and bond investments. Thrifts are failing in number. At their peak in the late 1960s, there were more iv,800. Simply a combination of factors, including sharp increases in involvement rates in the late 1970s and increased loan defaults during the recession of the early 1980s, has reduced their ranks significantly. Past year-terminate 2016, due mostly to acquisitions by or conversions to commercial banks or other savings banks, the number of thrifts had fallen to fewer than 800.
"FDIC-Insured Savings Institutions," https://www5.fdic.gov, accessed September 7, 2017.
| Peak Ten Insured U.S.-Chartered Commercial Banks, Based on Consolidated Assets, 2016 | |
|---|---|
| Bank | Consolidated Assets |
| one. JP Morgan Chase & Co. | 2,082,803,000 |
| 2. Wells Fargo & Co. | 1,727,235,000 |
| three. Banking concern of America Corp. | one,677,490,000 |
| four. Citigroup | 1,349,581,000 |
| five. U.S. Bancorp | 441,010,000 |
| 6. PNC Financial Services Grouping | 356,000,000 |
| seven. Capital One Financial Corp. | 286,080,000 |
| 8. TD Bank Due north America | 269,031,000 |
| ix. Bank of New York Mellon Corp. | 257,576,000 |
| 10. Land Street Banking concern and Trust Corp. | 239,203,000 |
Rating Banks: Mobile and Branch Banking a Must
Which banks provide the best customer satisfaction? J.D. Power (JDP), based in Costa Mesa, California, ranked 136 major banks in 11 U.S. regions based on responses from more than 78,000 retail cyberbanking customers. In the research visitor's 2017 U.S. Retail Banking Satisfaction Study, pinnacle performers received high ratings in account data, channel activities (such as branch, mobile, website, and ATM), fees, problem resolution, and production offerings.
While specific banks took the peak spots in various areas of the country, the overall customer sentiment in the JDP survey was clear: consumers wants banks that offer both digital experience and personal interaction in local branches—and the ones that tin make these two channels piece of work together effortlessly will be the most successful, especially among millennials. Findings also suggest banks that provide a convenient digital experience will attract and retain customers, and this digital experience must work seamlessly with a local branch system as younger customers avail themselves of other banking services such as mortgages and wealth management in the futurity. Other fundamental survey findings include:
- Regardless of historic period group, more than customers than always are using mobile cyberbanking.
- More than than 70 pct of all customers visited a local branch an average of fourteen times over the past twelvemonth, and their overall satisfaction was 27 index points higher than those who did not visit a bank co-operative.
- Close to 65 percent of bank customers have mobile payment services linked to their accounts.
- Successful problem resolution is a central driver of client satisfaction, and younger customers adopt to resolve issues online or via social media.
Assessing customer satisfaction is also the goal of the American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI), which granted Citibank the acme spot in the national depository financial institution category in its almost recent survey, with a 12 percent spring in its overall score. Other top super regional banks in the ACSI written report include BB&T, Fifth 3rd Depository financial institution, Capital One, and Citizens Bank. Overall, national banks improved their overall client feel the most, up more than 6 per centum from ACSI's previous survey.
Sources: "Digital, Co-operative, Drive-Through or ATM? Yes, Delight! Say Bank Customers in J.D. Power Study," http://www.jdpower.com, accessed September eleven, 2017; ACSI: Customer Satisfaction with Banks, Insurance Rebounds, http://world wide web.theacsi.org, accessed September 11, 2017; American Bankers Association, "Millennials and Banking," https://www.aba.com, accessed September 11, 2017; Tanya Gazdik, "Citibank Leads National Banks in Written report," https://www.mediapost.com, November 15, 2016.
Disquisitional Thinking Questions
- What can banks and financial institutions do to retain their customers and make them feel valued?
- Is there a cost involved in non making customer service a priority? Explain your answer.
Credit Unions
A credit spousal relationship is a non-for-profit, member-owned fiscal cooperative. Credit union members typically take something in mutual: they may, for example, piece of work for the same employer, belong to the aforementioned wedlock or professional group, or nourish the same church or school. The credit spousal relationship pools their avails, or savings, in order to make loans and offer other services to members. The not-for-profit status of credit unions makes them revenue enhancement-exempt, so they can pay proficient interest rates on deposits and offer loans at favorable involvement rates. Like banks, credit unions tin have either a country or federal charter.
The approximately 5,700 credit unions in the U.s.a. take more than than 108 million members and over $1.34 trillion in assets. The five largest credit unions in the Usa are shown in (Figure). Although the U.S. credit spousal relationship system remained potent during the 2007–2009 financial crisis, consumer-owned credit unions in several regions weakened as a result of home foreclosures, business organisation failures, and unemployment rates. Today, the credit union organisation continues to demonstrate its resilience as the economy continues to rebound.
"A Brief History of Credit Unions," and "Industry at a Glance as of 3/31/17," https://www.ncua.gov, accessed September 7, 2017.
Services Offered
Commercial banks, thrift institutions, and credit unions offer a wide range of financial services for businesses and consumers. Typical services offered by depository financial institutions are listed in (Figure). Some financial institutions specialize in providing fiscal services to a particular blazon of customer, such as consumer banking services or business banking services.
Banks Have on P2P Payments
Person-to-person (P2P) payment systems are big business organization, and U.South. banks are now working together to compete in this billion-dollar industry. P2P transfers made through mobile apps such as Venmo, PayPal, Foursquare Cash, and others accounted for more than than $147 billion in digital payments in 2016, according to recent research by the Aite Group.
The simplicity of P2P apps has made them a part of everyday life for millions, especially millennials and young adults who utilise their smartphones for many daily activities. Venmo, for example, requires merely a phone number and email in order for someone to transfer money to a friend (and the friend creates a Venmo account to receive payment). Social media sites also encourage their members to transfer money via mobile apps, such as Google Wallet and Facebook Messenger.
Banks accept been successful allowing their own customers to transfer money via apps; still, P2P transfers have been limited to other customers of the aforementioned bank—until now. A consortium of more than than xxx banks recently introduced a mobile app chosen Zelle, which tin can be used by anyone to transfer funds to customers across these banking institutions.
A downside of using Venmo is that information technology may take a day or ii for money to go far in a recipient's account because the coin flows through an intermediary. With Zelle, the transfer of money between two accounts will occur instantaneously, making payments happen quickly. For now, most banks using Zelle are making the service gratis of accuse—knowing that information technology is in their all-time interest to drift people to a cashless and checkless environs, which volition eventually lower their costs in terms of services, labor, overhead, etc.
Is a cashless society imminent now that major banks have gotten on board with P2P payments? Probably non, simply the cyberbanking industry's delivery to challenging Venmo and other digital payment systems somewhen may result in a stronger acquirement stream and underscores their business strategy of staying continued to customers of all ages.
Critical Thinking Questions
- Does working together on a P2P organization help banks stay competitive? Explain your reasoning.
- Practice you retrieve P2P payment systems volition eventually eliminate the utilize of cash in our society? Why or why not?
Sources: "Use Venmo with Anyone," https://venmo.co, accessed September 12, 2017; Sarah Perez, "Zelle, the U.S. Banks' Venmo Rival, Will Launch Its Mobile App Next Week," Tech Crisis, https://techcrunch.com, September 8, 2017; Kevin Wack, "Zelle Says 4M Users Have Enrolled Since June Launch," American Banker, https://www.americanbanker.com, September 8, 2017; Jennifer Surane, "Venmo Killer? Banks Roll Out Faster P2P Payments with Zelle," Bloomberg Technology, https://www.bloomberg.com, June 12, 2017; James Rufus Koren, "Equally Millennials 'Venmo' Each Other Coin, Banks Fight Back with Their Own Mobile Apps," Los Angeles Times, http://www.latimes.com, March 27, 2017.
| 5 Largest U.Southward. Credit Unions |
|---|
|
Nondepository Financial Institutions
Some financial institutions provide certain banking services but do not have deposits. These nondepository financial institutions include insurance companies, alimony funds, brokerage firms, and finance companies. They serve both individuals and businesses.
Insurance Companies
Insurance companies are major suppliers of funds. Policyholders make payments (chosen premiums) to purchase fiscal protection from the insurance visitor. Insurance companies invest the premiums in stocks, bonds, real manor, concern loans, and existent estate loans for large projects.
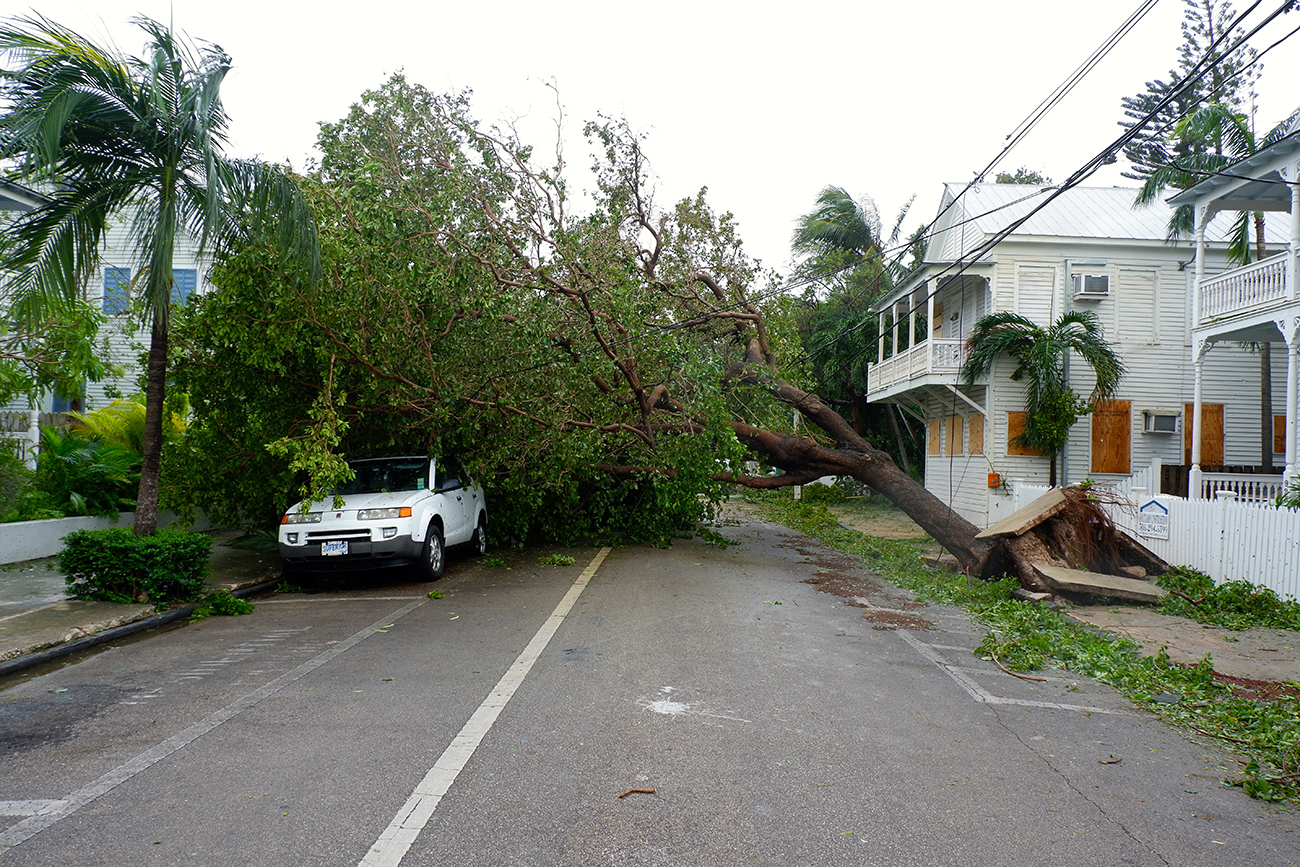
Insurance companies, hurt by billions of dollars in unforeseen payouts during natural disasters such as Hurricane Irma in 2017, are rethinking their reliance on ending-hazard modelers, whose run a risk estimates failed to conceptualize cataclysmic storms such as Hurricanes Katrina, Irma, and Harvey. True cat-chance businesses forecast potential weather-related expenses for insurers through sophisticated computer modeling that analyzes historical meteorological data. How do frequent natural disasters touch on insurance companies and their policyholders? (Credit: Cayobo/ Flickr/ Attribution 2.0 Generic (CC BY 2.0))

| Services Offered by Depository Financial Institutions | |
|---|---|
| Service | Description |
| Savings accounts | Pay involvement on deposits |
| Checking accounts | Allow depositors to withdraw any amount of funds at any time up to the corporeality on deposit |
| Money market place eolith accounts | Savings accounts on which the interest rate is set at marketplace rates |
| Certificates of deposit (CD) | Pay a higher involvement rate than regular savings accounts, provided that the deposit remains for a specified period |
| Consumer loans | Loans to individuals to finance the purchase of a home, car, or other expensive items |
| Business loans | Loans to businesses and other organizations to finance their operations |
| Electronic funds transfer | Utilise of computers and mobile devices to conduct financial transactions |
| Automated teller auto (ATM) | Allows bank customers to brand deposits, withdrawals, and transfers from their accounts 24 hours a day |
| Debit cards | Allow customers to transfer money from their bank account straight to a merchant'due south account to pay for purchases |
| Online banking | Allows customers to acquit fiscal transactions via the net or through a dial-in line that operates with a bank'due south software |
| Mobile apps | Technology that allows consumers to download programs to mobile devices that enable them to take care of banking, fiscal, and other transactions |
| Direct deposit of paychecks | Enabled through employers and payroll service vendors; allows financial institutions to have directly deposits of payroll checks to consumers' checking and/or savings accounts on a regular basis |
Alimony Funds
Corporations, unions, and governments set up aside large pools of money for later use in paying retirement benefits to their employees or members. These pension funds are managed past the employers or unions themselves or by outside managers, such as life insurance firms, commercial banks, and private investment firms. Alimony plan members receive a specified monthly payment when they reach a given historic period. After setting aside enough money to pay near-term benefits, pension funds invest the residual in business organization loans, stocks, bonds, or existent estate. They often invest large sums in the stock of the employer. U.S. pension fund assets total nearly $iii.4 trillion.
"U.S. Public Alimony Avails Rise to $3.396 Trillion in Q4—Census," http://world wide web.reuters.com, March 30, 2017.
Brokerage Firms
A brokerage house buys and sells securities (stocks and bonds) for its clients and gives them related advice. Many brokerage firms offer some banking services. They may offer clients a combined checking and savings account with a high interest rate and also make loans, backed by securities, to them.
Finance Companies
A finance company makes brusque-term loans for which the borrower puts upward tangible assets (such as an automobile, inventory, machinery, or property) as security. Finance companies oftentimes make loans to individuals or businesses that cannot become credit elsewhere. Promising new businesses with no track record and firms that can't get more credit from a banking company oftentimes obtain loans from commercial finance companies. Consumer finance companies make loans to individuals, often to embrace the lease or buy of large consumer goods such as automobiles or major household appliances. To compensate for the actress adventure, finance companies unremarkably charge higher interest rates than banks.
- What is the financial intermediation process?
- Differentiate between the three types of depository financial institutions and the services they offering.
- What are the 4 main types of nondepository financial institutions?
Summary of Learning Outcomes
- What are the primal financial institutions, and what office practice they play in the process of financial intermediation?
Financial institutions can be divided into 2 primary groups: depository institutions and nondepository institutions. Depository institutions include commercial banks, thrift institutions, and credit unions. Nondepository institutions include insurance companies, alimony funds, brokerage firms, and finance companies. Fiscal institutions ease the transfer of funds between suppliers and demanders of funds.
Glossary
- banking company charter
- An operating license issued to a depository financial institution past the federal authorities or a state authorities; required for a commercial banking company to practise business.
- commercial banks
- Turn a profit-oriented financial institutions that accept deposits, brand business and consumer loans, invest in authorities and corporate securities, and provide other fiscal services.
- credit unions
- Non-for-profit, member-owned fiscal cooperatives.
- financial intermediation
- The process in which financial institutions act equally intermediaries between the suppliers and demanders of funds.
- pension funds
- Large pools of money set bated past corporations, unions, and governments for later use in paying retirement benefits to their employees or members.
- thrift institutions
- Depository institutions formed specifically to encourage household saving and to brand home mortgage loans.
Which Institution Offers Banking Services But Do Not Accept Deposits Like Traditional Banks,
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/businessopenstax/chapter/u-s-financial-institutions/
Posted by: ceballosanctinget.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Institution Offers Banking Services But Do Not Accept Deposits Like Traditional Banks"
Post a Comment